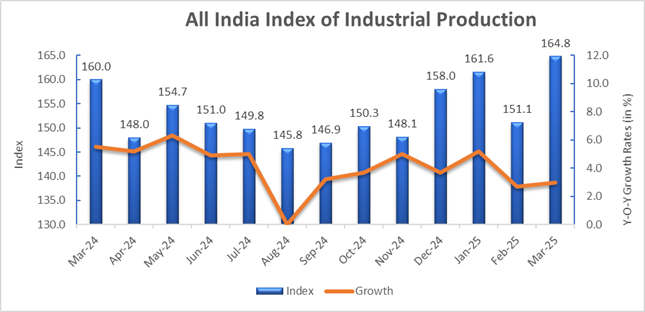
India’s domestic policy framework remains strong, bolstering economic growth as income tax cuts take effect and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) continues rate reductions, industry experts said. The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) saw an uptick to 3% in March, compared to 2.9% in February, reflecting stable industrial recovery.
The power sector recorded 6.3% growth, while the mining sector lagged behind, registering a modest 0.4% increase, according to data from the Ministry of Statistics. Infrastructure and construction goods showed notable improvements, with 8.8% IIP growth in March, signaling that government capital expenditure gained momentum toward the fiscal year’s end.
Consumer durables rebounded, rising to 6.6% from 3.7%, driven by easing food inflation and improved purchasing power. Export-oriented sectors, including textiles, machinery, and petroleum products, saw accelerated growth, possibly due to frontloaded shipments ahead of reciprocal tariffs. The computers and electronic products segment recorded a 21.5% surge, up from 11.2%, reinforcing India’s expanding footprint in new-age exports.
Mahendra Patil, Founder and Managing Partner, MP Financial Advisory Services, remarked that FY25 IIP growth of 4% reflects stable industrial performance as the economy transitions toward broader normalization.
“While industrial growth has moderated, the broader economy remains robust,” he stated, citing stable core sectors, resilient tax revenues, and controlled inflation as key drivers of sustained growth into FY26. With inflation under control, the RBI retains scope for continued accommodative policy, provided global uncertainties do not escalate.
India’s economic trajectory remains strong, supported by a normal monsoon outlook and lower crude oil prices, reinforcing domestic stability despite external challenges. Experts anticipate continued expansion in key sectors, ensuring steady progress into the next fiscal year.